
XInvoice
XInvoice is a standard format for electronic invoices in Germany. It was developed to simplify and standardise the exchange of invoice data between companies and the public administration.
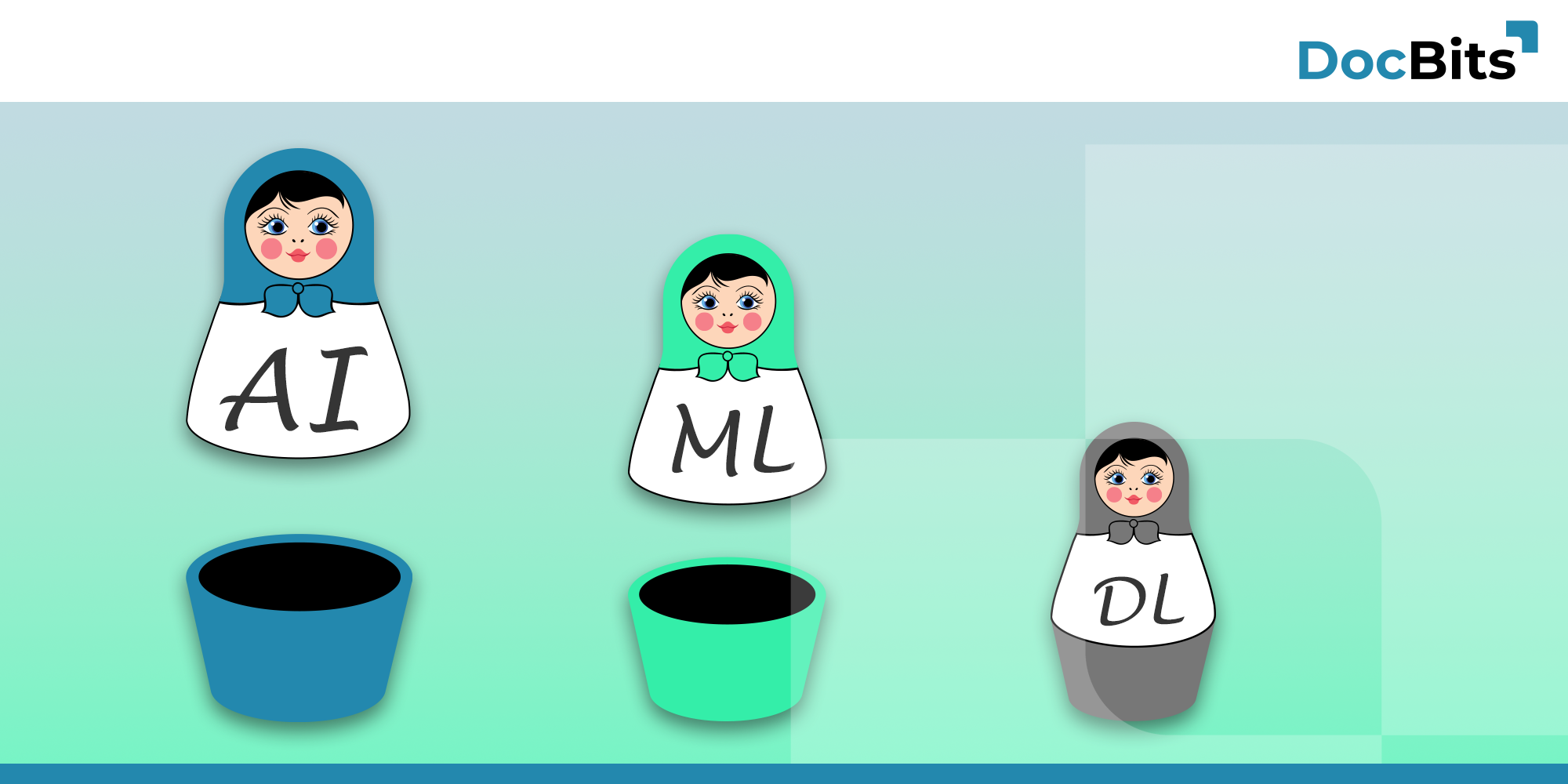
Today’s world revolves around data – from analyzing massive data sets to predicting trends. In this era of digitization and automation, machine learning (ML) is at the center of it all. But what exactly is machine learning, how does it work, and how does it differ from artificial intelligence (AI)? Let’s dive in and find answers to these questions.
Machine learning is an area of artificial intelligence that allows computers to learn from experience without being explicitly programmed. Imagine teaching a child to recognize an animal. Initially, you show him pictures of different animals and tell him which animal is in the picture. Over time, the child learns to identify the animals on his own by recognizing similarities and differences in the pictures. Machine learning works similarly, except instead of the child, there is a computer and instead of pictures, data is used.
A classic example of machine learning is spam email detection. Initially, spam filters had to be manually programmed to recognize specific words. With ML algorithms, spam filters can now learn by analyzing thousands of emails. They recognize patterns such as common spam terms or suspicious senders to identify future spam emails. Over time, the algorithm continues to improve its ability to detect spam.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the overarching term that refers to the creation of systems that exhibit human-like intelligence. Machine learning is a subset of AI. While AI covers the concept of intelligence, machine learning refers to the method by which machines/systems develop that intelligence, namely by learning from data.
Machine learning has a wide range of applications. It can be used in image recognition to make cars self-driving, in medical diagnosis to detect diseases early, in financial analysis to predict markets, and in many other areas. It allows machines to recognize patterns and make decisions that can surpass human abilities.
There are different types of machine learning, including supervised learning, in which the algorithm is trained with labeled data; unsupervised learning, in which the algorithm finds patterns in unlabeled data; and reinforcement learning, in which the algorithm learns how to act in a given environment through rewards and punishments. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages and is suitable for different tasks.
Machine learning has a wide range of applications. It helps voice assistants like Siri and Alexa understand human speech. It’s used in medicine to improve diagnoses; in finance to detect fraud; in the automotive industry to develop self-driving cars; and in advertising to create personalized recommendations. Even in agriculture, ML is used to predict optimal planting times. These are just a few examples.
Share:

XInvoice is a standard format for electronic invoices in Germany. It was developed to simplify and standardise the exchange of invoice data between companies and the public administration.

Validation Validation in data processing: importance and advantages Validation plays a critical role in data processing to ensure the quality, accuracy and reliability of data. In this glossary article, we’ll

A smart home is a house or similar facility where appliances and devices can be controlled remotely from anywhere with an internet connection.

Return on investment (ROI) is a key concept in the world of corporate finance. This indicator serves as a benchmark for the profitability of investments and plays a decisive role in strategic decisions made by companies.

IDP What is “PPS”? PPS stands for Production Planning and Control System. This is a computer program/software tool designed to help companies plan, control and monitor production, as well as

A pitch is a summary of your story/business idea in a single sentence (max. In one paragraph) – also called a high-concept.